Sudong Filter Press Manufacturer:專注過(guò)濾設(shè)備制造,源頭實(shí)力值得信賴
在選擇壓濾設(shè)備時(shí),靠譜的廠家不僅意味著質(zhì)量保障,更代表售后服務(wù)與技術(shù)支持的穩(wěn)定性。作為專業(yè)的Sudong Filter Press廠家,我們堅(jiān)持以“專注制造、穩(wěn)定輸出”為核心理念,致力于為各行業(yè)客戶提供高效、安全、耐用的固液分離解決方案。
蘇東壓濾機(jī)廠家坐落于工業(yè)資源豐富、配套成熟的長(zhǎng)三角地區(qū),擁有多年行業(yè)經(jīng)驗(yàn)、先進(jìn)加工設(shè)備以及專業(yè)技術(shù)團(tuán)隊(duì)。無(wú)論是污水處理廠、化工企業(yè),還是食品加工廠,我們都能根據(jù)客戶不同的工藝要求,推薦最合適的壓濾機(jī)型號(hào),并支持定制開發(fā)。
我們能為您提供:
? 直供價(jià)格,去中間環(huán)節(jié):真正的源頭廠家,產(chǎn)品出廠價(jià)直供全國(guó)。
? 多種類型壓濾機(jī)可選:板框式、廂式、自動(dòng)拉板、隔膜壓濾機(jī)等全系列。
? 經(jīng)驗(yàn)豐富的工程師團(tuán)隊(duì):可提供選型、布置方案、安裝調(diào)試一站式服務(wù)。
? 快速響應(yīng)的售后體系:質(zhì)保期內(nèi)免費(fèi)技術(shù)指導(dǎo),終身配件供應(yīng)保障。
如果您正在尋找一家值得長(zhǎng)期合作的壓濾機(jī)廠家,歡迎聯(lián)系蘇東壓濾機(jī)廠家,我們將為您提供專業(yè)可靠的產(chǎn)品與服務(wù),共同推動(dòng)工業(yè)生產(chǎn)效率提升。
]]>- 定期檢查泵和電機(jī):檢查泵和電機(jī)的外觀是否正常,有無(wú)磨損、變形、損壞等情況。檢查泵和電機(jī)的連接是否牢固,螺栓是否緊固。
- 檢查泵的密封:檢查泵的密封件是否磨損、老化、損壞,密封效果是否良好。如果密封件損壞,需要更換新的密封件。
- 檢查泵的潤(rùn)滑:檢查泵的潤(rùn)滑情況是否良好,潤(rùn)滑油是否充足,是否有漏油現(xiàn)象。如果潤(rùn)滑油不足或變質(zhì),需要更換新的潤(rùn)滑油。
- 檢查泵的進(jìn)出口壓力:檢查泵的進(jìn)出口壓力是否正常,壓力表是否準(zhǔn)確。如果壓力異常,需要調(diào)整泵的工作參數(shù)或檢修泵的密封件。
- 檢查泵的振動(dòng)和噪音:檢查泵的振動(dòng)和噪音是否正常,有無(wú)異常的振動(dòng)或噪音。如果振動(dòng)或噪音異常,需要檢修泵的軸承或密封件。
- 檢查泵的冷卻水:對(duì)于需要冷卻水的泵,檢查冷卻水是否充足、水質(zhì)是否干凈。如果冷卻水不足或水質(zhì)不好,需要更換或清理冷卻水。
需要注意的是,在進(jìn)行板框式壓濾機(jī)泵的常規(guī)檢查時(shí),需要遵循安全規(guī)范和操作說(shuō)明,確保檢查過(guò)程的安全性和準(zhǔn)確性。
]]>Slurry treatment equipmentIn recent years, it has been used in the construction of subways and real estate in large and medium-sized cities, and the mud generated during the construction will pollute the cityscape, basic agricultural land and underground water. Construction mud is mainly produced by the following types of projects: drilled pile construction mud is produced by rotary drilling rigs, forward and reverse cycle drilling rigs, percussion drilling rigs and other drilling methods; underground continuous wall construction mud is produced by continuous wall, double-wheeled milling and other equipment to form a trench; mud and water shield construction mud is produced by the mud and water balanced shield tunnel construction; non-excavation construction mud is produced by horizontal directional drilling and mud and water pipe jacking construction. Construction mud consists of liquid and clay, supplemented by additives, and is mainly used to protect the hole wall and carry the drill cuttings out of the hole. In the process of drilling, due to the drilling slag constantly entering into the mud, the specific gravity, viscosity and sand content of the mud change, and cannot meet the requirements of mud performance, it must be purified, that is, the solid-liquid separation and then the drilling slag in the mud is separated and circulated for use. At present, a large amount of waste mud is generated during and after the operation cycle of diaphragm wall and pile foundation construction. The waste mud contains clay minerals such as montmorillonite and rock debris, and its consistency is so large that it can neither be discharged directly, nor can it settle naturally within a short period of time. If not treated in time, it will not only affect the construction, but also cause environmental pollution or water pollution and other secondary public hazards, such as the waste slurry is difficult to degrade in the natural state, which will cause soil crusting in the surrounding areas, salinisation of the soil, and massive destruction of vegetation; the waste slurry accumulates and infiltrates into the sub-surface layer of the groundwater for a long period of time, or flows into the rivers and creeks along with the spillage of rainwater, which will pollute the water sources and endanger the people's health; and the waste slurry piles up in the vicinity of the construction site, which will occupy large amounts of cultivated land or grassland. Waste slurry piled up around the construction site occupies a large amount of arable land or grassland, so that the occupied land loses its use value and becomes a new source of pollution. At present, there are more and more researches on waste slurry treatment in China, and the main treatment methods include chemical solidification treatment method, land cultivation treatment method, solid-liquid separation treatment method, etc. Among them, the solid-liquid separation treatment method is the most suitable method for the treatment of waste slurry. Among them, the solid-liquid separation method is relatively simple, the produced water can be discharged directly, and the discharged dry mud can be landfilled, which is especially suitable for the treatment of drilling mud in municipal underground projects. This paper gives an overview of domestic solid-liquid separation mud treatment equipment on the basis of extensive research, and designs a new type of mobile mud treatment equipment.
1 common domestic slurry treatment equipment
At present, the main mechanical equipment used to treat slurry by solid-liquid separation methods include vibrating screens, cyclone slurry purifiers and horizontal screw centrifuges.
1.1 Vibrating screens use high-frequency vibration to separate the solid particles in the slurry flowing through the screen cloth. Vibrating screen cloth is available in a variety of mesh sizes, with 100 mesh (separating particles with a diameter of 0.15 mm or larger) or coarser cloth generally used, and 200 mesh being the densest cloth used. Vibrating screens are generally located at the front end of the process and are mainly used to treat large solid phases.
1.2 Cyclone slurry purifier After pumping the slurry into the cyclone, the slurry will be restricted by the shape of the cyclone and produce high speed cyclone. Under the action of centrifugal force, the solid phase with higher density than the liquid will be leaning against the wall of the cylinder, while the liquid with lower density will be in the middle of the cylinder, so that the coarser particles will be separated out from the slurry. Cyclone mud purifier solves the problem of recycling mud on site, improves the efficiency of mud recycling, and saves cost, but it does not solve the problem of disposal of waste mud.
1.3 Horizontal screw centrifuge is the only solid-liquid separation device that can remove the free liquid on the surface of solid-phase particles. The larger the rotational speed of the centrifuge, the smaller the particle size of the solid phase particles that can be separated, and when the rotational speed of the centrifuge reaches 3200 r-min-1, the smallest particle size that can be separated is 2 μm. The centrifuge is generally located at the end of the treatment process, and it is mainly used to treat small particles of solid phase. According to the particle size and particle size grading of the solid phase substances in the slurry, and considering the performance requirements of the treated slurry, different treatment processes can be selected, but the order of treating the large particles first and the small particles second must be followed. Since the working principle of horizontal screw centrifuge is to separate solid and liquid by using the centrifugal force generated by mass difference, it is necessary to pre-treat the slurry, that is to say, to add flocculants to destroy the colloidal structure of the slurry and form the mass difference between the inner substances. Since there are many kinds of flocculants (anion, cation, organic flocculants, etc.), each of which has different effects on the soil, and the price of flocculants is high, generally RMB 20,000 yuan per tonne, and the quantity of pre-treatment is also large, about 5kg-m-3; therefore, the cost of using horizontal centrifuge is high, which is not conducive to the promotion of it.
2 Design of new mobile slurry treatment equipment
2.1 Design Principle The main structural parts of this equipment include screen filter head, slurry pump, vacuum tank, valve, hydraulic cyclone, diaphragm filter press, press system, backblowing system, automatic pulling plate system, belt machine. The specific work flow is as follows: firstly, the vacuum tank is filled with clean water, and the operator turns on the slurry pump start button, and the lead water in the vacuum tank is pumped out, which makes the vacuum tank generate negative pressure, and the slurry in the slurry tank is automatically sucked into the vacuum tank when the pressure is large enough to achieve continuous self-absorption of the slurry; when there is a need to recycle the slurry, the inlet to the valve of the hydraulic cyclone is turned on and the solid particles of the slurry, such as gravel with a large particle size, are filtered, and the slurry can be filtered to obtain a higher quality of the solid particles. When the cyclone valve is closed and the valve of the diaphragm filter press is activated, the slurry is fed to the filter chambers through the central aperture of the diaphragm filter press, and the slurry is filtered through the filter cloths in the filter chambers, and the filtered water is discharged through the discharge port to the clean water pool, while the solid particles are deposited on the filter cloths; the cake on the filter cloths reaches a high level after a certain period of time; the slurry is then recycled to the clean water pool. After a certain period of time, when the cake on the filter cloth reaches a certain thickness, the press pump starts, and the filtration process is automatically transferred to the pressing process, and the feeding is stopped at the same time; the high-pressure press pump sends the press water from the press tank to the diaphragm plate, and the elastic inner plate of the diaphragm plate bulges up, and squeezes uniformly with the formed cake, so as to further reduce the water content of the cake on the filter cloth; after the end of the pressing process, the press pump stops, and the press water is returned to the tank, and then the residual moisture in the centre orifice is blown out by the compressor using compressed air. After the press is finished, the press pump stops, the press water flows back to the water tank, and then the slurry remaining in the centre aperture is blown out by compressor air; the automatic pulling system is activated, and the filter plates are pulled apart one by one, the cakes are separated from the filter cloths and fall down to the belt machine at the bottom, which is started at the same time, and the cakes are discharged to the mud pit dug at the front end of the plant, and then shoveled away by a loader; then the filter cloths are cleared, and the next cycle is started, and the slurry treatment is completed. The core of this equipment is the filtration technology. Filter press technology originated in Europe and has been widely used in Germany and the UK in the petroleum, mining, coal, chemical and medical industries. After hundreds of years of development, the filtration technology has been continuously improved. As a solid-liquid separation technology, it has the advantages of good separation effect and wide applicability, especially for the separation of viscous and fine mixed liquids with unique superiority. Compared with other technologies, press filtration technology has the following features: small unit filtration surface area, high adaptability to materials, wide selection of filtration surface area, high filtration pressure, low cake water content, simple structure, easy operation, fewer failures, convenient maintenance, clear filtrate with high solid phase recovery after cake filtration, and stable filtration operation with no noise.
2.2 Design programme
2.2.1 Integral frame In order not to exceed the limit of highway transport and to facilitate the transfer, the overall size of this equipment is designed as 9.6m×3m×2.5m, and the integral frame is made of 100mm×100mm channel steel welded together, which mainly serves to connect the functional parts and facilitate lifting, and there is a steel mesh structured walkway around the frame for the convenience of workers, and there is a sun- and rain-protection shed on the top. The top is equipped with a sun- and rain-proof shed.
2.2.2 Vacuum self-priming units Vacuum self-priming units consist of a vacuum tank and a slurry pump.
(1) Vacuum tank. Considering the pressure of sucking up the slurry from the slurry tank, the capacity of the vacuum tank is set at 700L, with a filling port and an air vent at the top and a drain port at the bottom.
(2) slurry pump. Slurry pump not only to ensure that the work of the filter pressure (8bar), but also to consider the efficiency of the material into the problem, so choose the head of 80m, flow rate of 100m3-h-1 centrifugal pump.
2.2.3 Pressing mechanism The pressing mechanism of this equipment consists of hydraulic pump station, oil cylinder, pressing plate and voltage gauge.
(1) Cylinder. Considering that the filtration pressure is 8 bar during normal operation, the cylinder compression pressure should be 12-20 bar; so Φ350 cylinder is used.
(2) Electrical contact pressure gauge. When the hydraulic cylinder is being pressed, when the pressing force is greater than the setting value of the pressure sensor (16 bar), the relief valve starts to unload, the power supply of the hydraulic motor is cut off, and the pressing action is completed. When the compression force reaches the lower limit of the pressure gauge, the cylinder motor starts and the oil pump supplies oil to ensure continuous compression of the cylinder during the filtering process.
2.2.4 Filter Structure The filter structure consists of a diaphragm filter plate and filter cloth.
(1) Filtration method. There are two types of filtration methods: open flow and concealed flow, in order to ensure the compactness of the equipment structure and the cleanliness of the equipment during operation, the equipment adopts the concealed flow method, with liquid outlet holes at the corners of each filter plate, and four liquid outlet ports are connected together by pipes at the end of the equipment.
(2) Filter cloth. Filter cloth is the main filtration medium, and the selection and use of filter cloth have a decisive effect on the filtration effect. It is necessary to choose suitable filter cloth material according to the pH value, solid particle size, sand content and other factors of the filtering material, so as to realise lower filtration cost and higher filtration efficiency, and ensure that the filter cloth is smooth and not wrinkled in the process of use. Since the construction slurry is mainly alkaline, and considering the problems of cake release and efficiency, this equipment adopts nylon monofilament filter cloth with air permeability of 800L-m-2-s-1.
2.2.5 Press mechanism The press mechanism consists of a press pump, press tank and press hose.
(1) Press pump. Comparing the effect of pressing force on the water content of the cake and the cost of press plates available on the market, a diaphragm press plate with a pressure resistance of 12 bar was selected, and the working pressure of the press pump was set at 8 bar; the upper limit of the pressure gauge was set at 10 bar.
(2) Press tank. The working water consumption is about 3.5m3, so the volume of the press tank is 4m3.
2.3 Structural design and process design
(1) Design the product structure according to the design programme.
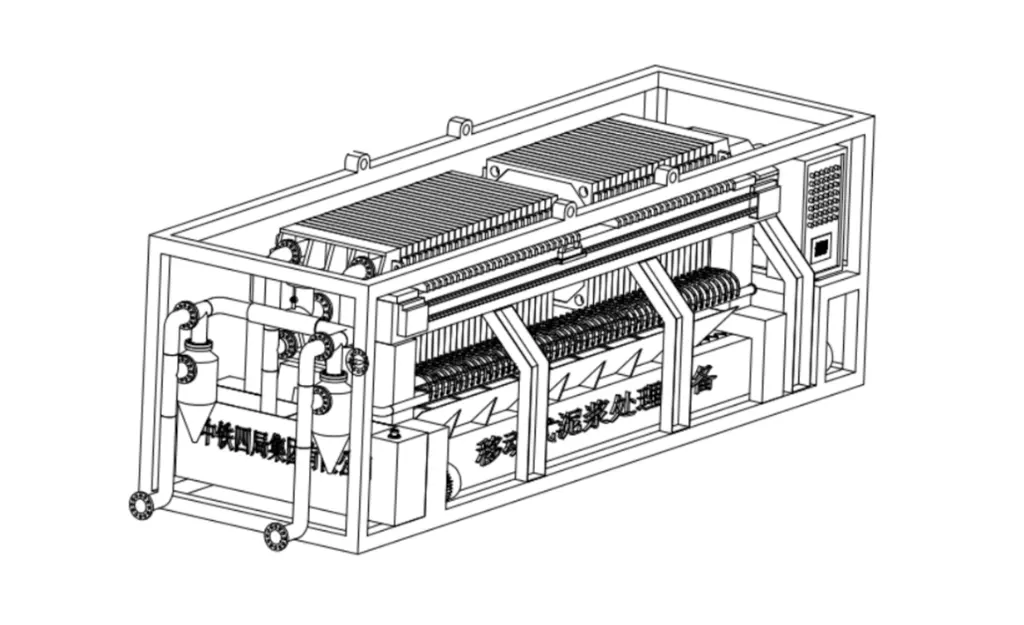
(2) Process design. Establish the process flow for the final treatment of slurry.
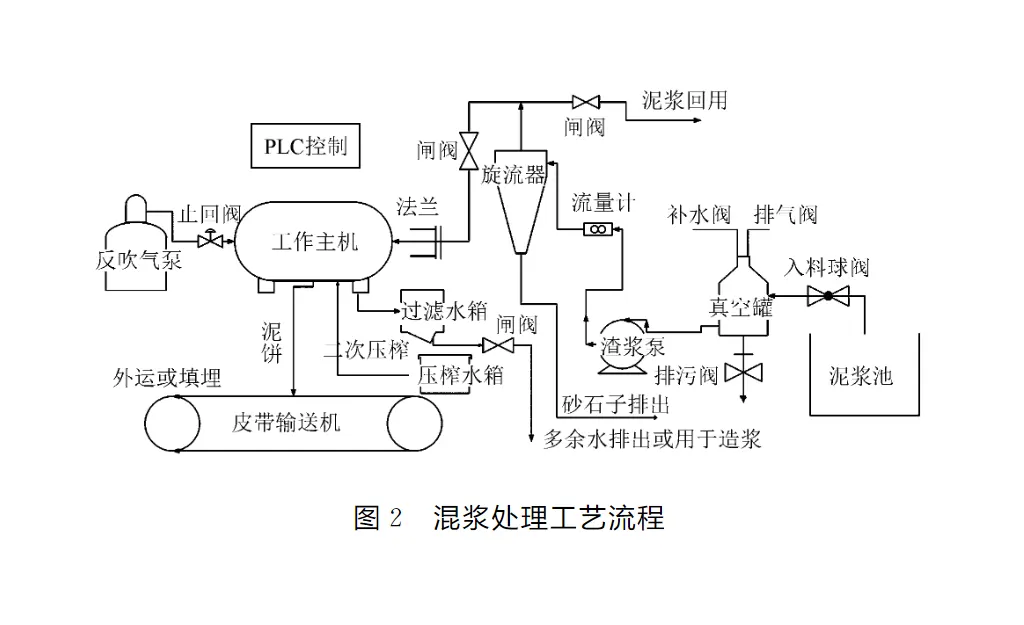
3 Engineering application and analysis and evaluation
3.1 Application of the project The project is based on the sixth standard section of the construction of the first phase of the R2 railway line in Jinan (Figure 3). According to the data of field research, the project mainly adopts the technology of diaphragm wall construction, in which 200-300m3 of mud slurry is used in one trench (generally 400m3 in consideration of the surplus), and the mud slurry is generally recycled 4-6 times during the operation, and the mud slurry used in one trench is recycled to produce about 55m3 of waste mud slurry in the end, and there may be 3-4 trench construction at the same time in the later stage when the working surface is opened up completely. The equipment will carry out the mud slurry according to the construction time. The equipment will treat the slurry accordingly to the construction time.

According to the data calculation, the waste slurry treatment capacity is 55~220m3-1, and the treatment time is 24h. The average daily waste slurry treatment capacity is 140m3. According to the present situation, the application of this equipment is good, and it basically achieves a flow process of 2h after steady operation, and the slurry treatment capacity is 20m3 in each flow process, and the water content of discharged clean water and solid cake is about 35%. The water content of discharged water and solid cake after treatment is about 35%.
3.2 Factors Affecting Treatment Effectiveness
(1) Factors affecting cake thickness. According to the processing situation, it can be seen that the thickness of dry cake is positively proportional to the filtration time when the concentration of feed slurry is fixed, but the thickness of cake does not increase obviously when the filtration time reaches 45min.
(2) Factors affecting the water content of mud cake. The water content of the cake is related to the pressing pressure, the higher the pressing pressure is, the lower the water content is, at the same time, through the test, it can be determined that it is appropriate to control the pressing time at about 30min.
3.3 Optimisation of inlet design In practice, it is found that the inlet of the equipment is often clogged, so the inlet is optimised to solve the problem of clogging of the inlet in case of highly concentrated slurry.
3.4 Analysing and evaluating
3.4.1 Calculation of slurry handling capacity
(1) Single-cycle slurry treatment volume. The size of the slurry tank is 3m×6m, the liquid level of the single-cycle slurry tank is 40cm, and the single-cycle slurry treatment volume is about 7.2m3.
(2) Single-cycle water discharge. According to the flowmeter that comes with the slurry treatment equipment on site, it can be known that: the maximum water discharge is 10.9m3-h-1 when feeding, the minimum water discharge is 1.2m3-h-1, the feeding time is 1h, the feeding and draining time is about 50min; the maximum water discharge is 2.2m3-h-1, the minimum water discharge is 1.0m3-h-1, the pressing time is 30min, the pressing and draining time is 30min. The maximum water discharge during pressing is 2.2m3-h-1, the minimum water discharge is 1.0m3-h-1, the pressing time is 30min, and the press drainage time is 30min.
(3) Single-cycle mud cake discharge volume. According to the actual situation, the size of mud cake is 1m×1m, the average thickness of mud cake is 2.5cm, the number of mud cake discharged from one cycle is 59, and the volume of mud cake discharged from one cycle is 1.48m3.
3.4.2 Comparison of slurry treatment costs
(1) Cost calculation of adopting the mud transport method in the construction organisation design. According to the cost calculation of the project department, adopting professional tanker truck to transport and treat the waste slurry, one tanker truck can transport 25m3 of waste slurry, and the unit price of one truck is about RMB 2,000 per time, and the unit cost of treatment is RMB 80m-m-3.
(2) Costing of mud treatment with this equipment. After preliminary calculations, the use of new equipment for on-site waste mud treatment, equipment machine power of about 50kW, according to the efficiency of 7.2m3-h-1 treatment of waste mud, time about 2h, power consumption of 100 degrees, according to the industrial electricity tariffs, a work with electricity costs about 100 yuan. After separation of mud and water, the water can be directly recycled for on-site construction, and the dry mud can be transported by dump trucks, and the cost of dump trucks is 40 RMB-m-3, and the transport cost is 59.2 RMB. According to this calculation, the cost of adopting new equipment for waste slurry treatment is 22.1 RMB-m-3. In summary, the cost of using this equipment to treat 1m3 slurry is 57.9 RMB less than that of transporting.
4 Conclusion
(1) In this paper, field tests were carried out on loess slurries with specific gravity ranging from 1.08 to 1.32, and the slurries with specific gravity greater than 1.2 needed to be pre-treated with filter to remove large sand particles, otherwise the inlet would be easily clogged. After adopting the screen filter, the inlet was not clogged, but there was cake layering because the specific gravity of the slurry was different during the feeding process, which was solved by adding a stirring device to the filter.
(2) After the second pressing and backblowing technology, the water content of the cake is around 35%, and the specific gravity of the slurry is 1.08, so the compression ratio of the slurry treatment is around 9:1.
(3) The equipment designed in this paper covers an area of about 25m2, it is necessary to do a good job in advance of the site hardening, for the mud pool is small and more dispersed, can consider the equipment for miniaturisation of the design, so as to reduce the cost of a single piece of equipment, and more convenient for the transfer of the site.
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author and the original source. Welcome to call us for consultation, technical exchanges, and material experiments.
Technical Consultancy: 188517-18517
]]>1 工程概況溫州市甌海區(qū)仙巖街道鳳池村城中村改造安置房建設(shè)項(xiàng)目,地下室開挖深度4 m左右,采用樁基礎(chǔ)(鉆孔灌注樁),鉆孔灌注樁共需施工691根。本工程地層復(fù)雜、樁基數(shù)量較大。為了保證如期完成施工任務(wù),投入14臺(tái)GPS-15型以上鉆機(jī)進(jìn)行樁基施工。本工程擬采用廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿固化工法施工,固化泥漿約46 958 m3。離出的泥餅含水率低,且運(yùn)行速度快。具有較好的脫水效果,具備場(chǎng)地條件的項(xiàng)目能大量進(jìn)行現(xiàn)場(chǎng)固化處理,減少運(yùn)輸過(guò)程的污染,節(jié)約固化時(shí)間。
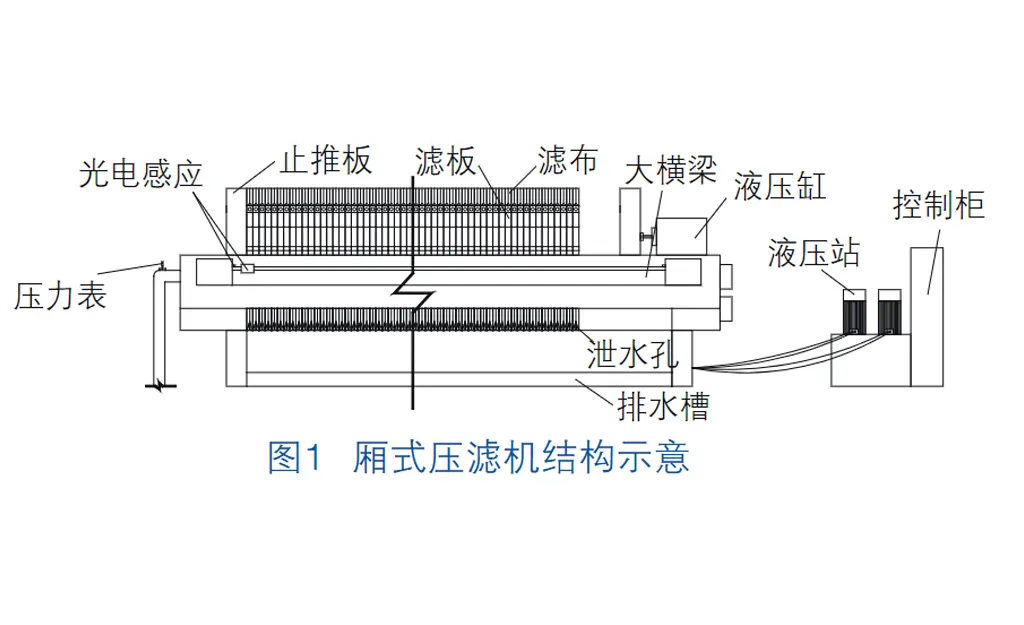
2 工法特點(diǎn)及適用范圍
1)本工法采用廂式壓濾機(jī)進(jìn)行泥漿過(guò)濾脫水固化,設(shè)備結(jié)構(gòu)簡(jiǎn)單、拆裝方便、機(jī)械化程度高,易操作,所分
2)相對(duì)泥漿外運(yùn),泥餅外運(yùn)處理成本較低,環(huán)境污染小。如溫州城區(qū)泥漿,往往需通過(guò)陸運(yùn)及水運(yùn)方式運(yùn)輸至集中消納地點(diǎn)處理,路程較遠(yuǎn),運(yùn)輸成本較高。采用本工法則大大減少了外運(yùn)的泥漿數(shù)量,道路沿途的滴、灑、漏污染及部門管控投入費(fèi)用也相應(yīng)減少。同時(shí),基本不用在消納場(chǎng)地再行固化,節(jié)約土地資源,減少生態(tài)環(huán)境污染。
3)分離出的泥土再進(jìn)行無(wú)害化處理后,還可深化加工利用。通過(guò)一系列技術(shù)改良措施,使廢棄的土方轉(zhuǎn)化為具有一定強(qiáng)度和滲漏性的填方材料;泥餅中的固相物有黏土和石屑,再加入水泥和砂子,配制成黏土水泥砂漿,并進(jìn)一步調(diào)整配方,改善養(yǎng)護(hù)條件,黏土砂漿完全可以滿足一般建筑要求;還有其他各種再利用方法,從而實(shí)現(xiàn)變廢為寶。
4)排出的清水用于循環(huán)打樁和洗車,節(jié)約工程用水,有利于環(huán)境保護(hù)。
5)本工法是工程建設(shè)中將廢棄泥漿通過(guò)專用機(jī)械設(shè)備深度脫水的工藝,適用于建筑工程泥漿護(hù)壁灌注樁泥漿處理、橋梁樁基工程泥漿處理、勘察鉆探泥漿處理、鉆井工程廢棄泥漿的無(wú)害化處理等。
3工藝原理在泥漿護(hù)壁灌注樁樁基施工過(guò)程中,安排適合的場(chǎng)地設(shè)置廂式Slurry Filter Press,并配套泥餅堆積外運(yùn)場(chǎng)地,按照施工現(xiàn)場(chǎng)實(shí)際泥漿日產(chǎn)量、泥漿日處理消耗量等要求,確定添置設(shè)備的規(guī)模。樁基施工過(guò)程產(chǎn)生的泥漿集中收集至儲(chǔ)漿池,儲(chǔ)漿池再集中將泥漿輸送至泥漿混合箱,通過(guò)加入一定比例的生石灰攪拌混合后,再輸送至廂式壓濾機(jī)進(jìn)行脫水固化,分離出泥土、其他固態(tài)物和清水。泥土等固化物堆積整理外運(yùn),清水可循環(huán)用于樁基鉆孔施工。最終達(dá)到節(jié)約用水、泥漿固化外運(yùn)、降低成本的目的。
4施工工藝流程及操作廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿固化工法的施工工藝流程。
4.1 施工準(zhǔn)備1)了解工地地勘資料、設(shè)計(jì)圖紙、相關(guān)規(guī)范等文件。
2)編制泥漿固化的專項(xiàng)施工方案,經(jīng)項(xiàng)目部審核、批集水池進(jìn)行混合攪拌準(zhǔn)備石灰外加劑汽車外運(yùn)施工準(zhǔn)備樁基濕作業(yè)成孔過(guò)程中的泥漿生成及循環(huán)使用泥漿匯集廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿壓榨清水匯集泥餅堆放工程現(xiàn)場(chǎng)道路灑掃除塵,加藥劑處理后排入市政管網(wǎng)等圖2廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿固化工法施工工藝流程示意準(zhǔn),報(bào)監(jiān)理、業(yè)主批準(zhǔn)實(shí)施。
3)設(shè)備進(jìn)場(chǎng)前,提供詳細(xì)參數(shù)、質(zhì)保資料及人員備案資料等。
4)計(jì)算泥漿量,選擇泥漿池、沉淀池、循環(huán)池布置位置并開挖,泥漿池按照樁基工程1 d完成的樁基成孔體積的3倍計(jì)算,再乘以充盈系數(shù),通常溫州地區(qū)取1.15。依照此標(biāo)準(zhǔn)可再適當(dāng)放大容量,以便在泥漿排出不及時(shí)的情況下可增加泥漿存儲(chǔ)量,保證施工進(jìn)度。
5)安排泥漿固化設(shè)備設(shè)置場(chǎng)地,進(jìn)行場(chǎng)地平整,設(shè)備基礎(chǔ)按專業(yè)設(shè)計(jì)圖紙施工,待基礎(chǔ)達(dá)到混凝土設(shè)計(jì)強(qiáng)度后,設(shè)備方可進(jìn)場(chǎng)安裝。
6)廂式壓濾機(jī)安裝完成后進(jìn)行調(diào)試,保證運(yùn)行正常。
4.2 泥漿生成及循環(huán)使用在施工過(guò)程中泥土與水混合產(chǎn)生泥漿,通過(guò)泥漿循環(huán),將樁身及底部泥漿、沉渣攜帶至沉淀池沉淀凈化,使泥漿達(dá)到一定的黏度、密度、含砂率,以滿足樁身護(hù)壁、攜渣、冷卻鉆具、潤(rùn)滑等施工要求。在滿足現(xiàn)場(chǎng)鉆孔施工所需護(hù)壁泥漿量的基礎(chǔ)上,多余泥漿進(jìn)行固化處理。
4.3 泥漿固化管線布置及匯集在樁機(jī)進(jìn)場(chǎng)施工前,項(xiàng)目部根據(jù)場(chǎng)地環(huán)境及施工部署要求,按照施工方案科學(xué)合理地設(shè)置泥漿固化管線。樁機(jī)在施工過(guò)程中產(chǎn)生的泥漿匯總排放至總泥漿池,可增設(shè)沉淀池用以沉淀沉渣。在總泥漿池架設(shè)泥漿泵,通過(guò)直徑至少為150 mm的輸送管連接至泥漿與生石灰匯集池(集水池),采用電磁流量計(jì)控制泥漿輸送量。泥漿與生石灰混合攪拌后,經(jīng)集水池輸送至壓濾機(jī)進(jìn)行壓榨,產(chǎn)生的清水經(jīng)引流槽排至清水池。清水池再通過(guò)清水泵排放至樁機(jī)處循環(huán)施工或用于現(xiàn)場(chǎng)噴灑除塵、車輛沖洗等。
4.4 集水池混合攪拌泥漿與生石灰混合攪拌,在集水池中進(jìn)行融合。
1)泥漿池通過(guò)沉淀過(guò)濾后,濃度、密度需滿足固化要求。在濃度過(guò)低的情況下,應(yīng)將低濃度泥漿排向循環(huán)池循環(huán)使用,直至滿足固化要求后,再輸送至集水池。
2)工程現(xiàn)場(chǎng)采用30 t容積的生石灰罐,每天可固化泥漿618 m3。經(jīng)流量表測(cè)得每天消耗生石灰3.75 t,每立方米泥漿消耗生石灰6 kg,生石灰與泥漿充分?jǐn)嚢枞诤希?jīng)過(guò)化學(xué)反應(yīng),可起到吸水板結(jié)的作用。周 莉、閆相明、周星中: 應(yīng)用廂式壓濾機(jī)進(jìn)行樁基廢棄泥漿固化處理
4.5 廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿壓榨
4.5.1進(jìn)料壓榨廂式壓濾機(jī)過(guò)濾部分由按一定次序排列在主梁上的濾板、夾在濾板之間的濾布組成,濾板與濾布相間排列,形成了若干獨(dú)立的過(guò)濾單元——濾室。過(guò)濾開始時(shí),料漿在進(jìn)料泵的推動(dòng)下,經(jīng)止推板上的進(jìn)料口進(jìn)入各濾室,并借進(jìn)料泵產(chǎn)生的壓力進(jìn)行過(guò)濾。由于濾布的作用,固體留在濾室內(nèi)形成濾餅,濾液由水嘴(明流)或出液閥(暗流)排出。若需洗滌濾餅,可由止推板上的洗滌口通入洗滌水進(jìn)行洗滌;若需要較低含水率的濾餅,同樣可從洗滌口通入壓縮空氣,穿過(guò)濾餅層,以帶走濾餅中的部分水分。
4.5.2清水過(guò)濾及泥餅出料
1)通過(guò)泥漿壓榨,清水從濾板側(cè)邊水嘴流向設(shè)置好的水槽,水槽再外排至清水池。
2)經(jīng)壓榨固化的泥餅通過(guò)人工控制按鈕,以每塊濾板5 s的速度松板卸泥,本工程采用1500型程控液壓廂式壓濾機(jī),濾室容積為8 m3,每臺(tái)設(shè)備有濾板125塊,一次循環(huán)可固化處理22.5 m3泥漿,用時(shí)1 h,產(chǎn)生7.5 m3泥餅,卸泥時(shí)間需要15 min,泥餅落入下方的泥餅堆放場(chǎng)地,定時(shí)清運(yùn)。
4.6 泥餅及清水處理
1)每日通過(guò)現(xiàn)場(chǎng)配備的挖機(jī)收集泥餅并集中堆放,定期通過(guò)渣土車清運(yùn)至外場(chǎng)指定地點(diǎn)消納,以滿足現(xiàn)場(chǎng)施工要求,也可用于資源繼續(xù)加工再利用。
2)經(jīng)過(guò)6級(jí)處理的清水可排放至清水池,繼續(xù)用于樁基工程循環(huán)施工,也可用于現(xiàn)場(chǎng)道路噴灑除塵、洗清等。含有氫氧化鈣的廢水不能直接用于飲用或土壤農(nóng)業(yè)灌溉等,經(jīng)過(guò)藥劑中和處理,并檢測(cè)合格后可排放至市政管網(wǎng)。
3)另外,因黏土中堿的質(zhì)量分?jǐn)?shù)高達(dá)2.5%~2.7%,砂巖中堿的質(zhì)量分?jǐn)?shù)為0.1%~0.3%,在樁基鉆進(jìn)施工過(guò)程,過(guò)濾水如長(zhǎng)期循環(huán)使用,會(huì)增加水中堿的質(zhì)量分?jǐn)?shù),且在樁基混凝土澆搗過(guò)程中,因水泥本身含有K O H、NaOH等堿活性骨料,堿的質(zhì)量分?jǐn)?shù)過(guò)高會(huì)影響樁基混凝土的施工質(zhì)量,使混凝土產(chǎn)生較大的內(nèi)應(yīng)力,導(dǎo)致結(jié)構(gòu)破壞,產(chǎn)生裂縫,影響耐久性。參照J(rèn)GJ 63—2006《混凝土用水標(biāo)準(zhǔn)》,工程用水水質(zhì)要求堿質(zhì)量濃度≤1 500 mg/L,堿質(zhì)量濃度檢測(cè)應(yīng)符合GB/T 176—2017《水泥化學(xué)分析方法》中關(guān)于KOH、NaOH測(cè)定的火焰光度計(jì)法的要求。水質(zhì)取樣不少于5 L,再生水應(yīng)在取水管(出水口)終端接取,送至實(shí)驗(yàn)室測(cè)定,每個(gè)月做1次檢測(cè)。如檢測(cè)水堿質(zhì)量分?jǐn)?shù)過(guò)高,達(dá)不到繼續(xù)循環(huán)使用要求,可加水稀釋,達(dá)到要求后方可投入使用。
5效益分析
5.1 社會(huì)效益
1)節(jié)能環(huán)保。泥漿固化施工工法減少了泥漿排放量,土方可再生利用,處理后的水可進(jìn)行再循環(huán)施工,節(jié)約了工程用水,很好地保護(hù)了環(huán)境。
2)文明、美觀。泥漿固化施工工法使施工場(chǎng)區(qū)能更好地保持整潔美觀,便于日常場(chǎng)區(qū)清理,避免了以前鉆孔灌注樁樁基施工時(shí)場(chǎng)地泥漿外溢、環(huán)境臟亂的現(xiàn)象,更好地響應(yīng)文明施工的要求。
5.2 經(jīng)濟(jì)效益現(xiàn)以溫州市甌海區(qū)仙巖街道鳳池村城中村改造安置房項(xiàng)目為例,將廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿固化后的土方外運(yùn)效益與傳統(tǒng)的泥漿外運(yùn)效益進(jìn)行對(duì)比。經(jīng)過(guò)成本對(duì)比分析,溫州市甌海區(qū)仙巖街道鳳池村城中村改造安置房工程采用了廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿固化施工工法,與普通泥漿外運(yùn)施工工藝相比,在沒(méi)有影響施工效率的前提下,通過(guò)施工工藝,在土方外運(yùn)的前提下,省去了泥漿外運(yùn)處理,節(jié)約了相關(guān)費(fèi)用支出共計(jì)109 571元。可見,廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿固化施工工法具有可觀的經(jīng)濟(jì)效益,有很好的推廣前景。
6結(jié)語(yǔ)采用泥漿固化施工工法后,在一定程度上緩解了泥漿外排的壓力,固化后的多余土方可堆放在場(chǎng)地內(nèi),進(jìn)行覆蓋后臨時(shí)堆放,節(jié)約了成本,保證了施工進(jìn)度,取得了良好的應(yīng)用效果。在文明施工要求日益趨于嚴(yán)格的當(dāng)下,廂式壓濾機(jī)泥漿固化施工工法為類似有樁基工程的施工項(xiàng)目提供了一種可借鑒的廢棄泥漿處理方法。
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author and the original source. Welcome to call us for consultation, technical exchanges, and material experiments.
Sludge Filter Press,污水經(jīng)過(guò)沉淀處理后會(huì)產(chǎn)生大量污泥,既使經(jīng)過(guò)濃縮及消化處理,含水率仍高達(dá),體積很大,難以消納處置,必須經(jīng)過(guò)脫水處理,提高泥餅的含固率,以減少污泥堆置的占地面積。一般大中型污水處理廠均采用機(jī)械脫水。脫水機(jī)的種類很多,按脫水原理可分為真空過(guò)濾脫水、壓濾脫水及離心脫水三大類。本文就國(guó)內(nèi)污水處理廠經(jīng)常選用 的壓濾機(jī)包括帶式壓濾機(jī)及板框式壓濾機(jī)和離心式脫水機(jī)的工作原理、設(shè)備選型時(shí)需重點(diǎn)考慮的問(wèn)題以及維護(hù)運(yùn)行成本等作一介紹。
帶式壓濾脫水機(jī)帶式壓濾脫水機(jī)是由上下兩條張緊的濾帶夾帶著污泥層,從一連串有規(guī)律排列 的輥壓筒中呈形經(jīng)過(guò),依靠濾帶本身的張力形成對(duì)污泥層的壓榨和剪切力,把污泥層中的毛細(xì)水?dāng)D壓出來(lái),獲得含固量較高的泥餅,從而實(shí)現(xiàn)污泥脫水。一般帶式壓濾脫水機(jī)由濾帶、輥壓筒、濾帶張緊系統(tǒng)、濾帶調(diào)偏系統(tǒng)、濾帶沖洗系統(tǒng)和濾帶驅(qū)動(dòng)系統(tǒng)構(gòu)成。作機(jī)型選擇時(shí),應(yīng)從以下幾個(gè)方面加以考慮濾帶。要求其具有較高的抗拉強(qiáng)度、耐曲折、耐酸堿、耐溫度變化等特點(diǎn),同時(shí)還應(yīng)考慮污泥的具體性質(zhì),選擇適合的編織紋理,使濾帶具有 良好的透氣性能及對(duì)污泥顆粒的攔截性能。輥壓筒的調(diào)偏系統(tǒng)。一般通過(guò)氣動(dòng)裝置完成。濾帶的張緊系統(tǒng)。一般也 由氣動(dòng)系統(tǒng)來(lái)控制。濾帶 張力一般控制在一,常用值為。帶速控制。不 同性質(zhì)的污泥對(duì)帶速的要求各不相同,即對(duì)任何一種特定的污泥都存在一個(gè)最佳的帶速控制范圍,在該范圍內(nèi),脫水系統(tǒng)既能保證一定的處理能力,又能得到高質(zhì)量的泥餅。帶式壓濾脫水機(jī)受污泥負(fù)荷波動(dòng)的影響小,還具有出泥含水率較低且工作穩(wěn)定、能耗少、管理控制相對(duì)簡(jiǎn)單、對(duì)運(yùn)轉(zhuǎn)人員的素質(zhì)要求不高等特點(diǎn)。同時(shí),由于帶式壓濾脫水機(jī)進(jìn)人國(guó)內(nèi)較早,已有相當(dāng)數(shù)量 的廠家可以生產(chǎn)這種設(shè)備。在污水處理工程建設(shè)決策時(shí),可以選用帶式壓濾機(jī)以降低工程投資。目前,國(guó)內(nèi)新建的污水處理廠大多采用帶式壓濾脫水機(jī),例如北京高碑店污水處理廠一期工程五臺(tái)脫水機(jī)全部是帶式壓濾脫水機(jī),自投人運(yùn)行以來(lái)情況 良好,所以在二期設(shè)備選型時(shí)仍然選用了這種機(jī)型。
離心式脫水機(jī)離心脫水機(jī)主要由轉(zhuǎn)毅和帶空心轉(zhuǎn)軸的螺旋輸送器組成,污泥由空心轉(zhuǎn)軸送入轉(zhuǎn)筒后,在高速旋轉(zhuǎn)產(chǎn)生的離心力作用下,立即被甩人轉(zhuǎn)毅腔內(nèi)。污泥顆粒比重較大,因而產(chǎn)生的離心力也較大,被甩貼在轉(zhuǎn)毅內(nèi)壁上,形成固體層水密度小,離心力也小,只在固體層內(nèi)側(cè)產(chǎn)生液體層。固體層的污泥在螺旋輸送器的緩慢推動(dòng)下,被輸送到轉(zhuǎn)毅的錐端,經(jīng)大大改善運(yùn)行人員的工作環(huán)境,因而受到業(yè)轉(zhuǎn)毅周圍的出口連續(xù)排出,液體則由堰口溢 界人士的青睞。流排至轉(zhuǎn)毅外,匯集后排出脫水機(jī)。
板框式壓濾脫水機(jī)離心脫水機(jī)最關(guān)鍵的部件是轉(zhuǎn)毅,轉(zhuǎn)毅板框式壓濾機(jī)是通過(guò)板框的擠壓,使污的直徑越大,脫水處理能力越大,但制造及運(yùn) 泥內(nèi)的水通過(guò)濾布排出,達(dá)到脫水目的。它行成本都相當(dāng)高,很不經(jīng)濟(jì)。轉(zhuǎn)毅的長(zhǎng)度越主要由凹人式濾板、框架、自動(dòng)一氣動(dòng)閉合系長(zhǎng),污泥的含固率就越高,但轉(zhuǎn)毅過(guò)長(zhǎng)會(huì)使性統(tǒng)、側(cè)板懸掛系統(tǒng)、濾板震動(dòng)系統(tǒng)、空氣壓縮能價(jià)格比下降。使用過(guò)程中,轉(zhuǎn)毅的轉(zhuǎn)速是 裝置、濾布高壓沖洗裝置及機(jī)身一側(cè)光電保一個(gè)重要的控制參數(shù),控制轉(zhuǎn)毅的轉(zhuǎn)速,使其護(hù)裝置等構(gòu)成。設(shè)備選型時(shí),應(yīng)考慮以下幾既能獲得較高的含固率又能降低能耗,是離個(gè)方面心脫水機(jī)運(yùn)行好壞的關(guān)鍵。目前,多采用低對(duì)泥餅含固率的要求。一般板框式速離心脫水機(jī)。在作離心式脫水機(jī)選型時(shí),壓濾機(jī)與其他類型脫水機(jī)相比,泥餅含固率因轉(zhuǎn)輪或螺旋的外緣極易磨損,對(duì)其材質(zhì)要 最高,可達(dá),如果從減少污泥堆置占地有特殊要求。新型離心脫水機(jī)螺旋外緣大多 因素考慮,板框式壓濾機(jī)應(yīng)該是首選方案。做成裝配塊,以便更換。裝配塊的材質(zhì)一般框架的材質(zhì)。為碳化鎢,價(jià)格昂貴。
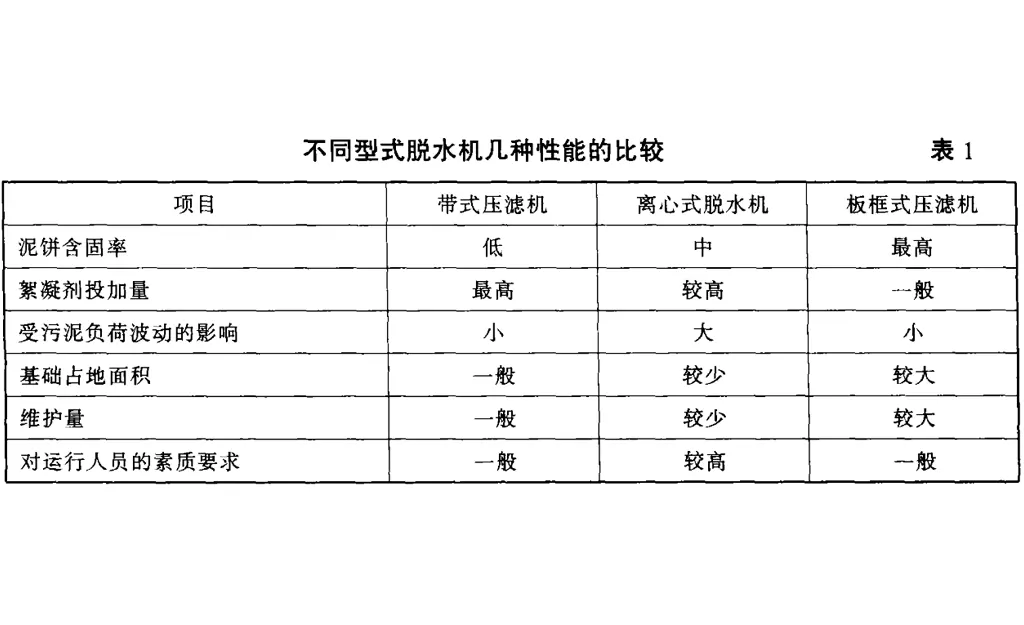
濾板及濾布的材質(zhì)。要求耐腐蝕,濾離心脫水機(jī)具有噪音大、能耗高、處理 布要具有一定的抗拉強(qiáng)度。能力低等缺點(diǎn)。國(guó)內(nèi)只有為數(shù)不多的幾個(gè)廠濾板的移動(dòng)方式。要求可以通過(guò)液家可以生產(chǎn)小型離心脫水機(jī),如果選擇大型壓一氣動(dòng)裝置全 自動(dòng)或半自動(dòng)完成,以減輕離心脫水機(jī),就只能依靠進(jìn)口,會(huì)增加工程 操作人員勞動(dòng)強(qiáng)度。投資,同時(shí),離心脫水機(jī)受污泥負(fù)荷的波動(dòng)濾布振蕩裝置,以使濾餅易于脫落。影響較大,對(duì)運(yùn)行人員的素質(zhì)要求較高,因與其他型式脫水機(jī)相比,板框式壓濾機(jī)此一般污水處理廠均不采用離心脫水工藝。最大的缺點(diǎn)是占地面積較大。以北京高碑店但近幾年來(lái),隨著科技進(jìn)步,離心式脫水機(jī)污水處理廠一期工程使用的帶式壓濾機(jī)和鞍的脫水技術(shù)在國(guó)外有了長(zhǎng)足進(jìn)展,例如瑞典山工業(yè)污水處理廠使用的板框式壓濾機(jī)為例公司生產(chǎn)的螺旋離心式脫水機(jī),作比較高碑店污水廠處理污水量為萬(wàn)其泥餅含 固率可達(dá)以上,而且操作是,污泥產(chǎn)量,干物質(zhì),采在全封閉的環(huán)境中進(jìn)行,脫水機(jī)周圍沒(méi)有任用五臺(tái)德國(guó)一型帶式壓濾機(jī),何污泥及污水存在,也沒(méi)有惡臭氣味,可以每臺(tái)壓濾機(jī)的基礎(chǔ)占地面積僅為鞍山污水廠處理污水量為萬(wàn),干物質(zhì),采用六臺(tái)板框式壓濾機(jī),每臺(tái)壓 濾 機(jī)的基礎(chǔ) 占地面積達(dá)。同時(shí),由于板框式壓濾機(jī)為間斷式運(yùn)行,效率低,操作間環(huán)境較差,有二次污染,國(guó)內(nèi)大型污水處理廠已很少采用。但近年來(lái),國(guó)外環(huán)保設(shè)備生產(chǎn)廠家在該機(jī)型上作了大量開發(fā)研制工作,使其適應(yīng)了現(xiàn)代化污水處理廠的要求,如通過(guò)系統(tǒng)控制就可以實(shí)現(xiàn)系統(tǒng)全自動(dòng)方式運(yùn)行,其壓濾、濾板的移動(dòng)、濾布的振蕩、壓縮空氣的提供、濾布沖洗、進(jìn)料等操作全部可以通過(guò)遠(yuǎn)端控制來(lái)完成,大大減輕了工人勞動(dòng)強(qiáng)度。小結(jié)根據(jù)不同型式脫水機(jī)性能的比較分析見表可以看出,不同的污水處理廠在作污泥脫水方案選擇時(shí),應(yīng)從污泥特性、運(yùn)行狀況、人員素質(zhì)、對(duì)泥餅的要求以及資金、成本等幾個(gè)方面綜合考慮,才能作出相對(duì)合理的選擇。
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author and the original source. Welcome to call us for consultation, technical exchanges, and material experiments.
Enquiry: 188517-18517
]]>
1煤用壓濾機(jī)的基本要求和特征
(1)設(shè) 備 大 型 化。采 用 大 型 濾 板 和 短 配 置 不 僅可 以 減 少 占 地,同時(shí)由于濾板組件變短導(dǎo)致壓差傳遞 次 數(shù) 減 少,壓 差 容 易 被 阻 斷,在 增 加 處 理 量 的 同時(shí)還可以減少因成餅不均勻所產(chǎn)生的危險(xiǎn)壓差。快開式壓濾機(jī)在濾板組件中間增加了金屬驅(qū)動(dòng)板,可徹 底 阻 斷 壓 差 的 傳 遞,延長(zhǎng)濾板和整個(gè)壓濾機(jī)的壽 命。
(2)運(yùn) 行 快 速 化。要 求 壓 濾 機(jī) 入 料 快、排 液快、卸 餅 快 以 及 更 換 濾 布 快,這就有利于大型壓濾機(jī) 采 用 多 端 口 入 料、明 暗 流 同 時(shí) 排 液、過(guò) 濾 面 設(shè) 計(jì)優(yōu) 化、縮短隔膜擠壓技術(shù)的過(guò)濾周期以及帶入料靴的 板 布 分 離 結(jié) 構(gòu) 等 措 施 的 實(shí) 現(xiàn)。而對(duì)于特大型的壓濾 機(jī),采用高位槽入料法更為合適。在 過(guò) 濾 初 期,選用高位自流的方法向壓濾機(jī)無(wú)障礙入料,實(shí) 現(xiàn) 快速 過(guò) 濾,無(wú) 需 進(jìn) 料 泵 可 以 大 大 節(jié) 省 能 耗;過(guò) 濾 后 期則 采 用 小 流 量 高 壓 泵,可 降 低 成 本。
(3)系 統(tǒng) 可 靠 性。在 使 用 壓 濾 機(jī) 時(shí),除 了 要 求液 壓 系 統(tǒng)、拉 板 系 統(tǒng)、洗布系統(tǒng)和集液翻板系統(tǒng)等可 靠 之 外,及時(shí)知道濾布的損壞情況和發(fā)現(xiàn)損壞濾布的確切位置對(duì)整個(gè)工藝的穩(wěn)定運(yùn)行也是非常重要的。將德國(guó)連恩舍過(guò)濾有限公司發(fā)明的三通取樣閥應(yīng) 用 到 壓 濾 機(jī) 中,可以在不影響工藝流程的情況下,精 確 發(fā) 現(xiàn) 損 壞 濾 布 的 確 切 位 置,避 免 濾 布 損 壞帶 來(lái) 的 一 系 列 問(wèn) 題。
2煤 用 壓 濾 機(jī) 及 濾 板 選 擇
2.1廂 式 壓 濾 機(jī)廂式壓濾機(jī)主要依靠入料泵提供的液壓驅(qū)動(dòng)力進(jìn) 行 脫 水,懸 浮 液 泵 入 壓 濾 機(jī) 后,首先在濾腔兩側(cè)的濾 布 表 面 形 成 濾 餅,然后不斷向?yàn)V腔中間增厚。連續(xù)液相的存在是保持液壓驅(qū)動(dòng)力的前提,所 以 濾餅 中 心 始 終 存 在 一 個(gè) 濃 度 高 于 入 料 濃 度、并 以 液 體為 連 續(xù) 相 的 固 液 混 合 體,俗 稱“囊 心”。“囊 心”的大 小 與 煤 泥 的 性 質(zhì)(如 顆 粒 大 小、灰 分、泥 化 程 度等)有 著 很 大 的 關(guān) 系。“囊 心”的 存 在 會(huì) 影 響 濾 餅的 水 分,并 阻 礙 卸 餅。對(duì) 于 相 同 的 煤 泥,采 用 高 壓入 料 可 減 小“囊 心”的 存 在,然而提高入料的壓力在 很 大 程 度 上 會(huì) 導(dǎo) 致 危 險(xiǎn) 壓 差 的 出 現(xiàn)。現(xiàn) 有 兩 個(gè) 途 徑 可 以 減 少 危 險(xiǎn) 壓 差 出 現(xiàn) 的 幾 率,一 是 通 過(guò) 增 加 濾 板 基 板 的 厚 度,二是通過(guò)增加濾板支 撐 凸 臺(tái) 的 數(shù) 量 或 直 徑。選 擇 壓 力 時(shí),通 常 要 考 慮濾 板 的 承 壓,目前濾板的壓力等級(jí)分為0.8MPa、1.6MPa和 更 高 壓 力3個(gè) 額 定 壓 力 檔 次。這 些 等 級(jí)均 是 在 常 溫 下 進(jìn) 行 分 類 定 義 的,忽略了溫度對(duì)濾板承 壓 能 力 的 影 響。
2.2隔 膜 壓 濾 機(jī)與廂式壓濾機(jī)的區(qū)別在于隔膜壓濾機(jī)中濾板有2個(gè) 可 前 后 移 動(dòng) 的 過(guò) 濾 面(隔 膜),當(dāng) 過(guò) 濾 工 序 完成 后,在隔膜與基板之間形成的擠壓腔中,通 入 擠壓 介 質(zhì)(如 壓 縮 空 氣 或 液 體),可對(duì)濾餅進(jìn)行二次擠 壓,使 得“囊 心”在二次擠壓的作用下均勻脫水,形成含水率更低和更加均勻的濾餅。由 于 隔 膜濾板擠壓的壓力與相鄰的隔膜濾板的工作壓力相等,二者壓力可以相互抵消,所 以 隔 膜 濾 板 即 使 在更高的二次擠壓作用下對(duì)濾餅進(jìn)行深度脫水時(shí)也不會(huì) 形 成 壓 差,不 會(huì) 造 成 濾 板 的 基 板 變 形。一 般 情 況 下,隔膜濾板的擠壓介質(zhì)采用壓縮空氣 或 不 可 壓 縮 液 體(例 如 水)。當(dāng) 擠 壓 壓 力 低 于0.8MPa時(shí),選 用 壓 縮 空 氣 較 多,主 要 原 因 是 由于0.8MPa的 空 壓 機(jī) 價(jià) 格 相 對(duì) 低 廉,選 擇 余 地 大,而且壓縮空氣單元的控制系統(tǒng)簡(jiǎn)單且成本較低;當(dāng)擠 壓 壓 力 大 于1.6MPa,使 用 壓 縮 空 氣 作 為 擠 壓 介質(zhì)的安全隱患較大,為 了 安 全 考 慮,不 可 壓 縮 液 體成 為 首 選。但是使用不可壓縮流體作為擠壓介質(zhì)時(shí)也 有 一 個(gè) 缺 點(diǎn),特 別 是 在 高 壓 擠 壓 完 成 前,由 于 濾餅的壓縮性近乎消失,擠 壓 壓 力 會(huì) 迅 速 升 高,為 了控 制 壓 力,設(shè) 計(jì) 的 壓 榨 單 元 較 為 復(fù) 雜,成 本 較 高。
2.3干 燥 壓 濾 機(jī)隨著對(duì)濾餅含水率的要求越來(lái)越低,僅靠提高隔膜擠壓壓力這種機(jī)械脫水方法已經(jīng)很難達(dá)到要求,此時(shí)干燥壓濾機(jī)應(yīng)運(yùn)而生。干燥壓濾機(jī)是將隔膜壓濾機(jī)和熱力干燥合二為一的一種設(shè)備,某些情況下可以將濾餅水分脫至1%以下,干燥壓濾機(jī)由機(jī)架、干 燥 濾 板(混 合 組 件)、加熱系統(tǒng)以及真空冷凝等系統(tǒng)組成。干燥濾板組中的隔膜濾板不作任何改變,而 其 中 廂式濾板的材料換成了導(dǎo)熱系數(shù)更高的金屬材料。由于 聚 丙 烯 隔 膜 濾 板 的 最 大 工 作 溫 度 為100°C,為 了提高干燥的溫差驅(qū)動(dòng)力,通 常 采 用 真 空 泵 將 過(guò) 濾 腔室 抽 至-10~-20kPa的 真 空 狀 態(tài),降 低 濾 液 的沸 點(diǎn)。同 時(shí) 采 用 加 熱 系 統(tǒng) 循 環(huán) 加 熱 水 至80°C~95°C,并從下端將水泵入干燥濾板,帶 盤 形 的 熱 水 流道的干燥濾板,以 保 證 干 燥 板 處 于 較 高 的 傳熱 溫 度,并 采 用 熱 力 學(xué) 的 方 法 降 低 濾 餅 水 分。在 干燥 階 段,必 須 保 持 隔 膜 處 于 擠 壓 狀 態(tài),保 證 濾 餅 始終完全緊貼干燥濾板,沒(méi) 有 空 氣 縫 隙,保 證 傳 熱 效率。如果隔膜沒(méi)有對(duì)濾餅進(jìn)行擠壓,就 會(huì) 隨 著 不 斷脫水 而 收 縮 變 薄,濾餅則有可能與干燥濾板脫離,導(dǎo)致濾餅處于懸空狀態(tài),干 燥 并 不 充 分。所 以 干 燥時(shí),壓濾機(jī)必須處于擠壓、加 熱、真 空 三 者 同 時(shí) 工作 的 狀 態(tài)。
2.4濾板與壓濾機(jī)的壓緊力當(dāng)濾板組件在壓濾機(jī)中壓緊時(shí),塑 料 的 濾 板 及濾 布 會(huì) 被 壓 縮,并且操作溫度的變化也會(huì)造成濾板及濾布材料的熱膨脹和冷收縮。由 于 有 很 大 的 伸 縮量,所 以 壓 緊 力 在 長(zhǎng) 度 方 向 上 應(yīng) 有 伸 縮 的 補(bǔ) 償 功能,這個(gè)伸縮補(bǔ)償功能主要由壓濾機(jī)的壓緊裝置來(lái)完 成。壓濾機(jī)的壓緊裝置所產(chǎn)生的壓力不僅要抵消過(guò) 濾 壓 力 和 擠 壓 壓 力,而且還必須保證過(guò)濾腔室的密 封 性,所 以 在 壓 濾 機(jī) 工 作 時(shí),必須保證有一個(gè)有效的 最 小 壓 緊 力Fmin,同時(shí)為了防止濾板的永久變形 和 機(jī) 架 的 過(guò) 載 損 壞,根據(jù)操作壓力和溫度的不同,必 須 將 壓 緊 力 限 制 在 最 大 壓 緊 力Fmax以 下。壓濾機(jī)的操作壓緊力必須介于Fmin和Fmax之 間。壓 緊力 太 小,會(huì) 導(dǎo) 致 板 間 漏 液,物 料 擠 出,而 極 端 情 況下 會(huì) 導(dǎo) 致 設(shè) 備 損 壞,還有可能影響人身安全。
濾 布 的 選 擇從 材 質(zhì) 上 講,聚丙烯的使用范圍最廣,耐 酸 堿性 優(yōu) 良,而且在市場(chǎng)上作為可選的透氣率范圍也最廣;尼 龍 濾 布 有 更 好 的 耐 磨 蝕 性 能,所 以 在 煤 泥 和精 煤 過(guò) 濾 中,一 般 尼 龍 布 作 為 首 選;滌 綸 布 則 能 在150°C的 溫 度 下 工 作,當(dāng) 然PEEK的 耐 溫 性 更 好,可 以 達(dá) 到200°C。一般情況下精煤過(guò)濾的濾布透氣率 在600~700L/m2·s,而 原 生 煤 泥 則 選 用 透 氣率 在250~400L/m2·s的 單 絲 尼 龍 濾 布。在 濾 布背 面 安 裝 大 透 氣 率 的 底 布,可延長(zhǎng)濾布的壽命10%~25%。對(duì)濾布做砑光處理可以減小其與濾餅的 實(shí) 際 接 觸 面 積,從而降低濾餅在濾布上的附著力,有 利 于 自 動(dòng) 卸 餅,同時(shí)砑光處理還可以將濾布的 透 氣 率 向 下 做 一 些 調(diào) 整。然而盡管過(guò)度的砑光處理 可 以 使 濾 布 的 表 面 更 加 光 滑,但對(duì)濾布的強(qiáng)度和壽 命 明 顯 有 害。
結(jié) 語(yǔ)
壓濾機(jī)作為煤泥水處理系統(tǒng)的把關(guān)設(shè)備,必 須具 有 設(shè) 備 大 型 化、運(yùn)行快速化和系統(tǒng)穩(wěn)定可靠等基本 特 征。隨著對(duì)泥餅含水率越來(lái)越低的要求,對(duì) 煤用 壓 濾 機(jī) 的 要 求 也 逐 步 提 高,干燥壓濾機(jī)應(yīng)運(yùn)而生并 逐 漸 在 煤 泥 脫 水 中 推 廣 應(yīng) 用。濾板是壓濾機(jī)的核心 部 件,過(guò) 濾 中 起 到 非 常 重 要 的 作 用,因 此 選 擇 濾板 時(shí),一定要綜合考慮溫度和壓力的影響。正 確 的壓緊力是保證壓濾機(jī)系統(tǒng)正常工作和使用壽命的一個(gè) 前 提,尼龍單絲濾布是煤礦用壓濾機(jī)的首選。
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author and the original source.
Welcome to call us for consultation, technical exchange, and material experiment.
]]>隨著各國(guó)對(duì)污水治理的日益重視和城市污水處理廠不斷新建,污泥的產(chǎn)量不斷地增長(zhǎng),污泥的快速有效處理已經(jīng)刻不容緩。污泥具有含水率高、含有大量病原體和微生物等有害生物、重金屬及有機(jī)物含量高等特點(diǎn),若在排放前不經(jīng)處理,則會(huì)對(duì)環(huán)境造成二次污染。通常情況下,污泥處理所需費(fèi)用高達(dá)整個(gè)污水治理廠建設(shè)和運(yùn)行費(fèi)用的50%~60%,因此,污泥的處理面臨著巨大的挑戰(zhàn)。污泥的處理原則是實(shí)現(xiàn)污泥的減量化、穩(wěn)定化、無(wú)害化和資源化,其中,污泥減量化無(wú)疑是污泥后續(xù)處理的關(guān)鍵及污泥處置的重點(diǎn)[3]。污泥減量化可有兩種途徑,一是減少污泥中有機(jī)物的含量,二是降低污泥的含水率。無(wú)論從技術(shù)還是資金方面來(lái)說(shuō),第2個(gè)途徑較第一個(gè)途徑簡(jiǎn)單易行,容易實(shí)現(xiàn)。污泥脫水的目的是除去污泥中大量的水分,從而縮小其體積,減輕其重量,以利于污泥的運(yùn)輸和進(jìn)一步處理。有研究顯示,如果將污泥含水率從99.3%左右降到60%~80%,其體積可降至原體積的1/10~1/15,大大地減少了污泥外運(yùn)的費(fèi)用及進(jìn)一步處理時(shí)產(chǎn)生的滲濾液量。時(shí)至今日,雖然污泥脫水理論和技術(shù)都取得了較大發(fā)展,但污泥脫水仍然是污水治理工程所面臨的一大技術(shù)性難題。本文從理論和技術(shù)2個(gè)方面歸納總結(jié)污泥脫水的發(fā)展特點(diǎn)和存在的問(wèn)題,從排水通道的角度重點(diǎn)分析了污泥脫水的微觀過(guò)程,認(rèn)為污泥脫水的微觀研究不能將污泥固體顆粒與水分隔開來(lái),而應(yīng)該以排水通道為“紐帶”將之視為一個(gè)整體,污泥脫水的微觀研究應(yīng)該注重從排水通道的角度去分析其淤堵機(jī)理。隨后著重介紹了國(guó)內(nèi)外污水處理廠的污泥脫水現(xiàn)狀,并基于多場(chǎng)聯(lián)合作用闡明污泥脫水的本質(zhì)、理論核心及技術(shù)核心,最后在總結(jié)了污泥脫水現(xiàn)狀的基礎(chǔ)上指出未來(lái)的研究與發(fā)展方向。
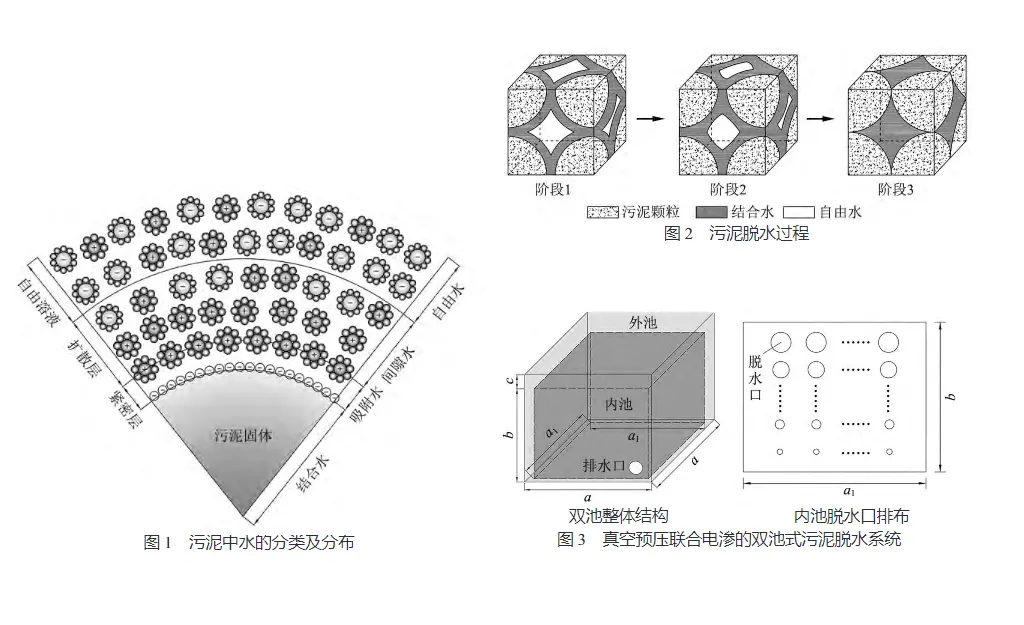
1污泥脫水理論及技術(shù)研究污泥的脫水是一個(gè)固-液分離過(guò)程,其基礎(chǔ)理論是在過(guò)濾、滲透、沉積等理論的基礎(chǔ)上發(fā)展起來(lái)的。污泥脫水的理論研究始于20世紀(jì)30年代。20世紀(jì)30-60年代,污泥脫水的理論研究主要在于基本理論的創(chuàng)立,具體表現(xiàn)為基本概念的提出、脫水模型的建立和修正。意識(shí)到只依靠機(jī)械外力脫水污泥難度大且效果不理想,提出了助濾的概念。后來(lái)出現(xiàn)的絮凝脫水、超聲波脫水、電滲析脫水等技術(shù),本質(zhì)上都屬于助濾的范疇。20世紀(jì)70-90年代,學(xué)者們逐漸將研究焦點(diǎn)從脫水模型轉(zhuǎn)向污泥的物理化學(xué)性質(zhì),并在物性分析的基礎(chǔ)上探討污泥脫水性能的影響因素,同時(shí)污泥調(diào)理改性技術(shù)開始發(fā)展。污泥的物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)如固體顆粒的尺寸、形狀、成分等受到了廣泛關(guān)注。在污泥物性研究基礎(chǔ)上,基于物理、化學(xué)及生物的污泥調(diào)理改性技術(shù)開始發(fā)展。但該時(shí)期的污泥調(diào)理改性研究停留在追求污泥脫水性能及效率在宏觀上的改善,缺乏微觀尺度上的調(diào)理改性機(jī)理分析。20世紀(jì)90年代開始,在污泥調(diào)理改性技術(shù)不斷發(fā)展的基礎(chǔ)上,電滲技術(shù)、絮凝技術(shù)和超聲波技術(shù)等受到關(guān)注。機(jī)械脫水替代自然干化成為污水治理廠的主要脫水技術(shù),但由于傳統(tǒng)的機(jī)械脫水方法效果不理想,新技術(shù)又有諸多缺陷不能及時(shí)克服,不少學(xué)者試圖從微觀尺度去解決難題,污泥中水的研究越發(fā)受到重視。實(shí)際上,早在1956年,就提出將污泥中的水分成自由水和結(jié)合水2種,但這樣簡(jiǎn)單的分類顯然不能滿足污泥脫水的研究。根據(jù)污泥固體顆粒與水的接觸關(guān)系將污泥中的水分成自由水、間隙水、吸附水和結(jié)合水4類(見圖1)。在接下來(lái)的20年中,許多學(xué)者對(duì)污泥中的水進(jìn)行了一系列理論及測(cè)試手段的研究,取得了大量成果,概括為幾個(gè)方面:污泥中水的分布特性,結(jié)合水含量測(cè)試技術(shù),結(jié)合水對(duì)污泥脫水性能影響。基于前人關(guān)于污泥中結(jié)合水的研究,一些學(xué)者以結(jié)合水為“橋梁”來(lái)改善污泥脫水性能,取得了良好效果。污泥的脫水與軟土的固結(jié)排水在本質(zhì)上有異曲同工之處,已有人關(guān)注到軟土固結(jié)排水過(guò)程中其微觀結(jié)構(gòu)的變化特征,而在污泥中此類研究還處于空白,從而導(dǎo)致對(duì)污泥脫水及其淤堵機(jī)理理解不夠深入,這也是真空預(yù)壓法廣泛用于軟土地基處理,而極少用于污泥脫水的原因。實(shí)際上,污泥脫水是一個(gè)污泥中的水在外力驅(qū)動(dòng)下克服淤堵從排水通道排出的過(guò)程,簡(jiǎn)化模型如圖2所示(便于討論,認(rèn)為污泥固體顆粒為球狀且不可壓縮,將污泥中的水分為自由水和結(jié)合水)。
隨污泥脫水的進(jìn)行(階段1→2→3),自由水不斷排出,同時(shí)排水通道也在不斷變化,相應(yīng)地,每個(gè)階段的淤堵機(jī)制也不一樣。階段1:排出的水主要為自由水,顆粒之間呈連通狀態(tài)的自由水作為排水通道;階段2:顆粒之間的自由水不再相互連通,排水通道的形成需要突破結(jié)合水的束縛,脫水難度較階段1增大,該階段有少量的結(jié)合水隨自由水排出;階段3:污泥中只剩下結(jié)合水,結(jié)合水的排出不僅要克服自身的束縛,還受固體顆粒的影響。雖然實(shí)際情況并不能完全由上述的簡(jiǎn)化模型說(shuō)明,但該模型表明污泥脫水的微觀研究不能將固體顆粒和水分隔開來(lái),而應(yīng)該以排水通道為“紐帶”將之視為一個(gè)整體。目前,研究者們往往將焦點(diǎn)集中在污泥絮體的特征、水的分布特征及含量測(cè)試、通過(guò)污泥調(diào)理改性手段降低結(jié)合水的含量等,缺乏對(duì)污泥脫水過(guò)程中污泥顆粒和水(尤其是結(jié)合水)的整體微觀分析及脫水機(jī)理探討,如脫水過(guò)程中排水通道的變化、脫水過(guò)程中的淤堵機(jī)理及改善途徑等。導(dǎo)致許多學(xué)者在研發(fā)新型脫水技術(shù)或設(shè)備時(shí),往往只注重宏觀上的脫水程度和脫水效率,缺乏基于污泥中固體顆粒與水微觀分析的淤堵機(jī)理研究,沒(méi)有從本質(zhì)上解決污泥脫水難的問(wèn)題。進(jìn)入21世紀(jì)后,圍繞“污泥深度脫水”這一主題,機(jī)械脫水技術(shù)得到不斷完善和改進(jìn),電滲脫水技術(shù)進(jìn)一步發(fā)展,基于物理、化學(xué)及生物技術(shù)的污泥調(diào)理改性手段成為研究熱點(diǎn)。在該時(shí)期,多技術(shù)的聯(lián)合使用受到關(guān)注,形成了許多以機(jī)械脫水為核心的多手段聯(lián)合技術(shù)。在室內(nèi)污泥機(jī)械脫水裝置上施加電場(chǎng),結(jié)果發(fā)現(xiàn)由于電場(chǎng)的作用,污泥中水分的去除率提高了10%~24%。研究了電磁場(chǎng)和化學(xué)調(diào)理后污泥的脫水性能,結(jié)果表明,二者聯(lián)合調(diào)理污泥的效果要優(yōu)于單獨(dú)調(diào)理,說(shuō)明磁場(chǎng)對(duì)污泥脫水性能有改善。則利用濾餅?zāi)P蛷睦碚撋戏治隽舜艌?chǎng)和壓濾改善固 – 液分離效果的機(jī)理,并指出磁場(chǎng)增強(qiáng)壓濾這一技術(shù)具有很大的應(yīng)用潛力[37]。國(guó)內(nèi)一些學(xué)者研究了不同污泥調(diào)理改性技術(shù)的聯(lián)合使用,如超聲波與絮凝劑、冷融調(diào)理與化學(xué)調(diào)理等[38-39]。鄧立新利用真空桶對(duì)污泥進(jìn)行脫水,并在污泥周圍和中部分別安置放電電極以形成環(huán)形電場(chǎng),初步論證了真空預(yù)壓聯(lián)合電滲脫水污泥的優(yōu)勢(shì)[40]。湯連生等人在此基礎(chǔ)上進(jìn)一步設(shè)計(jì)出真空預(yù)壓聯(lián)合電滲的雙池式脫水系統(tǒng),實(shí)現(xiàn)“內(nèi)池脫水,外池排水”。如圖3所示,整個(gè)脫水裝置分為內(nèi)池(a1×a1×b)和外池(a1×a1×(b+c))2個(gè)部分,外池底部設(shè)有排水口用于連接真空泵和排水,高出內(nèi)池的部分用作系統(tǒng)密封,在內(nèi)池底部和側(cè)壁安置網(wǎng)狀放電電極,同時(shí)在4個(gè)側(cè)壁上設(shè)計(jì)“上大下小”的脫水口(其位置和大小與放電電極相對(duì)應(yīng)),該系統(tǒng)通過(guò)改變放電電極的接入方式,實(shí)現(xiàn)電流場(chǎng)和滲流場(chǎng)的改變,從而使得污泥脫水更徹底,再者,側(cè)壁脫水口“上大下小”的設(shè)計(jì)方式充分利用了污泥的自重濃縮脫水,同時(shí)避脫水口處濾布受力不均的情況。隨后湯連生及其研究團(tuán)隊(duì)將熱水解脫水和閃蒸技術(shù)聯(lián)合,也取得了不錯(cuò)的效果。但在脫水設(shè)備的產(chǎn)業(yè)化上存在不足。總體上講,污泥脫水的多技術(shù)聯(lián)合使用本質(zhì)上屬于多場(chǎng)的聯(lián)合作用,已取得突破性進(jìn)展,但是,其脫水系統(tǒng)及設(shè)備的研發(fā)方面目前還處于進(jìn)一步探索和優(yōu)化階段。概括來(lái)說(shuō),污泥脫水理論及技術(shù)的研究大致經(jīng)歷這樣的發(fā)展趨勢(shì):從理論脫水模型到實(shí)際脫水設(shè)備、從宏觀脫水效率到微觀機(jī)理分析、從污泥物性影響脫水性能分析到污泥調(diào)理改性研究、從單一技術(shù)到多技術(shù)的聯(lián)合。雖然取得了可觀的理論成果,但缺乏與污泥的脫水實(shí)踐聯(lián)系,污水處理廠廣泛采用的機(jī)械脫水方式已經(jīng)無(wú)法滿足更有效的污泥處置方式,新型技術(shù)雖然具有很好的應(yīng)用前景,由于種種原因還未能得到廣泛應(yīng)用。
2污水處理廠污泥脫水現(xiàn)狀
20世紀(jì)80年代以前,各國(guó)都不太注重污泥的處理,污泥脫水主要采用自然干化。隨著城市化的發(fā)展,污泥產(chǎn)量劇增,各國(guó)開始重視污泥的脫水處理,機(jī)械脫水逐漸代替自然干化成為主要的污泥脫水方式。近年來(lái),污泥處理與處置過(guò)程中環(huán)境問(wèn)題的凸顯和對(duì)低成本低能耗的追求,各國(guó)愈發(fā)注重污泥的減量化和穩(wěn)定化,這無(wú)疑對(duì)污泥脫水提出了更高的要求。然而,污泥脫水實(shí)踐遠(yuǎn)遠(yuǎn)落后于理論研究,進(jìn)入21世紀(jì)以后,這種現(xiàn)象異常明顯。雖然各國(guó)的污水處理廠均設(shè)置了較為完善的污泥脫水設(shè)施,擺脫了初期的干化場(chǎng)和干化塘,但機(jī)械脫水仍然占據(jù)主導(dǎo)地位,污泥的成分、結(jié)構(gòu)復(fù)雜,直接進(jìn)行機(jī)械脫水往往達(dá)不到預(yù)期的處理效果。雖然電滲脫水、超聲波脫水和絮凝脫水等新技術(shù)已經(jīng)得到論證,但是由于造價(jià)和實(shí)施不便等原因沒(méi)能廣泛推廣運(yùn)用,并且我國(guó)污泥處置起步較晚,無(wú)論是制度還是技術(shù)都落后于發(fā)達(dá)國(guó)家。在國(guó)內(nèi),污泥脫水主要存在以下問(wèn)題:
1)重水輕泥。我國(guó)污水工程發(fā)展過(guò)程中長(zhǎng)期存在“重水輕泥”的情況[47]。大部分污水處理廠缺乏快速有效的污泥脫水設(shè)備,僅僅將污泥進(jìn)行簡(jiǎn)單濃縮處理后便外運(yùn),并未達(dá)到減量化、穩(wěn)定化要求。
2)脫水效率低,深度脫水工藝過(guò)于復(fù)雜。工程實(shí)踐已經(jīng)表明,傳統(tǒng)的機(jī)械脫水已經(jīng)遠(yuǎn)遠(yuǎn)無(wú)法滿足脫水要求,新型脫水技術(shù)(熱水解、超聲波、磁場(chǎng)、電場(chǎng)等)的引進(jìn)又需要污水處理廠支付高昂的費(fèi)用,且操作復(fù)雜[48]。然而,企業(yè)化經(jīng)營(yíng)模式導(dǎo)致追求最大的經(jīng)濟(jì)效益成為污水處理廠的根本目的。污泥脫水現(xiàn)狀與污泥脫水要求之間存在很大差距,所以利用低成本、廣泛運(yùn)用的技術(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)高效脫水污泥將是未來(lái)城市污泥脫水的有效出路。
3)污水處理分布化與污泥處理集約化矛盾加深,實(shí)現(xiàn)污泥的快速有效脫水迫在眉睫。胡維杰從工藝銜接的角度指出污泥處理與污水處理應(yīng)為一個(gè)有機(jī)的整。實(shí)際上,無(wú)論在效率還是模式上都應(yīng)該注重污泥處理與污水處理的有效銜接。首先,污水處理效率遠(yuǎn)遠(yuǎn)高于污泥處理,通常情況下,污水處理只需要短短數(shù)小時(shí),而污泥處理則耗時(shí)幾天,甚至幾個(gè)星期。所以,污水處理和污泥處理是隔離開的。其次,隨著污水處理廠的小型化和分布化,單個(gè)污水處理廠產(chǎn)生的污泥將相應(yīng)減少,污泥集約化處理模式成為首要選擇[52]。這就需要在污水處理廠引入快速有效的脫水技術(shù),以達(dá)到降低污水處理廠運(yùn)營(yíng)成本,同時(shí)又滿足污泥減量化、穩(wěn)定化的要求。縱觀國(guó)內(nèi)外污水處理廠的污泥脫水現(xiàn)狀,可以得知污泥脫水的生產(chǎn)實(shí)踐遠(yuǎn)遠(yuǎn)落后于理論研究,主要由以下2個(gè)原因?qū)е拢?/p>
1)理論研究往往集中在脫水效率、環(huán)保等方面,缺乏考慮技術(shù)成本和能耗,而污水處理廠的企業(yè)化運(yùn)作模式導(dǎo)致許多企業(yè)忽視污泥治理,更別說(shuō)污泥脫水了,導(dǎo)致一些看似完美的技術(shù)淪為空談;
2)許多污泥脫水技術(shù)雖然可行,但大多局限于理論分析和模型實(shí)驗(yàn)論證,很少結(jié)合污水處理廠的污泥脫水需求開展現(xiàn)場(chǎng)實(shí)驗(yàn)。
3多場(chǎng)聯(lián)合作用污水處理廠處理Sludge Filter Press脫水的典型流程是:污泥→預(yù)濃縮池→機(jī)械濃縮→機(jī)械脫水→泥餅。無(wú)論選用何種脫水技術(shù),污泥脫水的本質(zhì)就是通過(guò)特定的脫水設(shè)備實(shí)現(xiàn)固 – 液分離,在高含水率的濃縮污泥上施加作用場(chǎng)以得到低含水率的目標(biāo)污泥。筆者認(rèn)為,污泥脫水的理論核心是作用場(chǎng)之間以及作用場(chǎng)與污泥之間的相互作用,其技術(shù)核心是合理高效的脫水設(shè)備。從上述污泥脫水研究現(xiàn)狀及特點(diǎn)可以發(fā)現(xiàn),人們對(duì)理論核心的重視程度遠(yuǎn)遠(yuǎn)超過(guò)技術(shù)核心。目前,用于污泥脫水的作用場(chǎng)主要包括應(yīng)力場(chǎng)、溫度場(chǎng)、電場(chǎng)、化學(xué)場(chǎng)和磁場(chǎng)等。在以上作用場(chǎng)中,應(yīng)力場(chǎng)在現(xiàn)有污泥脫水技術(shù)中處于核心地位,而溫度場(chǎng)、電場(chǎng)、化學(xué)場(chǎng)及磁場(chǎng)多處于輔助地位,其中化學(xué)場(chǎng)和磁場(chǎng)常應(yīng)用于污泥深度脫水的預(yù)處理階段。應(yīng)力場(chǎng)具有獲取容易、實(shí)施簡(jiǎn)便等優(yōu)點(diǎn),也是人們最原始的脫水辦法,例如污泥在自重下排水固結(jié)(重力濃縮)、機(jī)械脫水等屬于應(yīng)力場(chǎng)的作用,而污泥自然干化則屬于溫度場(chǎng)的作用,電場(chǎng)作用脫水則是過(guò)去20年研究最多的技術(shù)。但在單一場(chǎng)作用下污泥的脫水效率太低,無(wú)論是脫水時(shí)間還是脫水效果,往往不能滿足污水處理廠的實(shí)際生產(chǎn)需求,這就需要應(yīng)力場(chǎng)與其它作用場(chǎng)的聯(lián)合作用。然而,現(xiàn)有理論、實(shí)驗(yàn)研究多集中于不同技術(shù)的聯(lián)合使用,而對(duì)場(chǎng)與場(chǎng)的相互作用缺乏更透徹的理解,污泥脫水過(guò)程中多場(chǎng)的耦合作用研究幾乎處于空白,所以未來(lái)污泥脫水研究的關(guān)鍵在于如何創(chuàng)新脫水設(shè)備以充分發(fā)揮各個(gè)作用場(chǎng)的優(yōu)勢(shì)。并且許多研究成果還停留在理論上的可行性,缺乏與污泥脫水實(shí)踐結(jié)合,也很少注重基于理論的污泥脫水設(shè)備研發(fā)與創(chuàng)新。
4結(jié) 語(yǔ)經(jīng)過(guò)不斷發(fā)展,污泥脫水已經(jīng)擺脫了早期的自然干化,在理論及技術(shù)上都取得了較大的進(jìn)步,機(jī)械脫水不斷完善,電滲技術(shù)、絮凝技術(shù)、超聲波技術(shù)及其它污泥調(diào)理改性手段受到廣泛關(guān)注和研究。由于成本、施工等因素,目前國(guó)內(nèi)外污水處理廠的污泥脫水方式仍以機(jī)械脫水為主。但機(jī)械脫水無(wú)法滿足更有效的污泥處置。所以,污泥脫水研究的重要內(nèi)容就是要改變“脫水實(shí)踐嚴(yán)重落后于理論研究”這一現(xiàn)狀。無(wú)論選取何種脫水技術(shù)和設(shè)備,污泥脫水的目的是實(shí)現(xiàn)污泥的減量化,其本質(zhì)是通過(guò)特定的脫水設(shè)備實(shí)現(xiàn)固 – 液分離,在高含水率的濃縮污泥上施加作用場(chǎng)以得到低含水率的目標(biāo)污泥。脫水過(guò)程的理論核心是作用場(chǎng)之間以及作用場(chǎng)與污泥之間的相互作用,其技術(shù)核心是合理高效的脫水設(shè)備。已有的污泥脫水理論和實(shí)驗(yàn)研究多集中在多技術(shù)的聯(lián)合使用,而缺乏對(duì)污泥脫水過(guò)程中多場(chǎng)的相互作用進(jìn)行透徹的分析,并且現(xiàn)有研究對(duì)污泥脫水理論研究的重視程度遠(yuǎn)超過(guò)脫水設(shè)備的研發(fā)。所以未來(lái)污泥脫水的關(guān)鍵是基于多場(chǎng)聯(lián)合理論創(chuàng)新污泥脫水設(shè)備以充分發(fā)揮各個(gè)作用場(chǎng)的優(yōu)勢(shì)。現(xiàn)有污泥脫水理論研究多集中于追求宏觀上的脫水效率,而對(duì)污泥脫水的微觀機(jī)理分析不夠透徹,從而導(dǎo)致不能從本質(zhì)上解決污泥脫水難的問(wèn)題。實(shí)際上,污泥脫水是水在外力驅(qū)動(dòng)下克服淤堵從排水通道排出的過(guò)程,隨著脫水過(guò)程的進(jìn)行,排水通道及相應(yīng)的淤堵機(jī)制都會(huì)發(fā)生變化,所以污泥脫水的微觀研究應(yīng)該注重從排水通道的角度分析其淤堵機(jī)理,這也是污泥脫水未來(lái)的重要研究方向。污泥脫水理論及技術(shù)經(jīng)歷了從理論脫水模型到湯連生等,污泥脫水研究現(xiàn)狀與新認(rèn)識(shí)實(shí)際脫水設(shè)備、宏觀脫水效率到微觀機(jī)理分析、污泥物性影響脫水性能分析到污泥調(diào)理改性研究、單一技術(shù)到多技術(shù)聯(lián)合使用的發(fā)展,取得了大量研究成果。實(shí)踐已經(jīng)證明,單一技術(shù)或設(shè)備無(wú)法滿足生產(chǎn)的要求,多技術(shù)的聯(lián)合使用已經(jīng)成為研究熱點(diǎn)。總體上講,多技術(shù)聯(lián)合使用本質(zhì)上屬于多場(chǎng)的聯(lián)合作用,已取得突破性進(jìn)展,但是,其脫水系統(tǒng)及設(shè)備的研發(fā)方面目前還處于進(jìn)一步探索和優(yōu)化階段。由于成本、施工等因素,因此污水處理廠的污泥脫水實(shí)踐嚴(yán)重落后于理論研究,還存在“重水輕泥”、脫水效率低下等問(wèn)題。從而導(dǎo)致許多新型污泥脫水技術(shù)淪為空談,所以利用低成本的、廣泛運(yùn)用的技術(shù)高效脫水污泥將是城市污泥脫水實(shí)踐的有效出路,而如何實(shí)現(xiàn)新型技術(shù)的產(chǎn)業(yè)化成為未來(lái)污泥脫水研究的重中之重。污水處理分布化與污泥處理集約化矛盾日益加深,如何在污水處理廠引入快速有效的污泥脫水技術(shù)亟待解決。
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author and the original source.
Welcome to call us for consultation, technical exchange, and material experiment.
]]>
The sealing surface of polymer filter plate is elastic contact with good sealing performance and high strength.
Applications:
It is widely used in metallurgy, chemical industry, printing and dyeing, ceramics, food, medicine, mining, coal washing and other industries.
Quality Assurance:
The goal is to ensure the quality of the product, using the system, all-round testing.
Reasonably priced:
With excellent products, reasonable price, to achieve the product increasebe on dutyObjective.
Honest co-operation:
Over the decades, we have earned a reputation for integrity and won the market.
Sales:181-181-000-11
Selection:188-517-18-517
Mailbox:suton@su-ton.com
]]>Polypropylene filter plates are modified with TPE elastomeric material for sealing and corrosion resistance.
Applications:
It is widely used in metallurgy, chemical industry, printing and dyeing, ceramics, food, medicine, mining, coal washing and other industries.
Quality Assurance:
The goal is to ensure the quality of the product, using the system, all-round testing.
Reasonably priced:
With excellent products, reasonable price, to achieve the product increasebe on dutyObjective.
Honest co-operation:
Over the decades, we have earned a reputation for integrity and won the market.
Sales:181-181-000-11
Selection:188-517-18-517
Mailbox:suton@su-ton.com
]]>Polypropylene reinforced filter plates are modified with TPE elastomeric material for sealing and corrosion resistance.
Applications:
It is widely used in metallurgy, chemical industry, printing and dyeing, ceramics, food, medicine, mining, coal washing and other industries.
Quality Assurance:
The goal is to ensure the quality of the product, using the system, all-round testing.
Reasonably priced:
With excellent products, reasonable price, to achieve the product increasebe on dutyObjective.
Honest co-operation:
Over the decades, we have earned a reputation for integrity and won the market.
Sales:181-181-000-11
Selection:188-517-18-517
Mailbox:suton@su-ton.com
]]>